Indoor Thermal Comfort
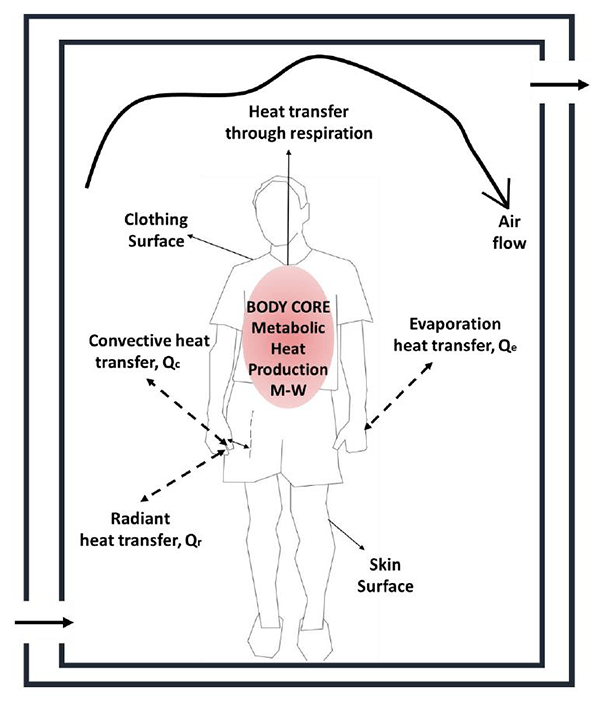
Thermal comfort; It is defined as “the condition of mind in which satisfaction is expressed with the thermal environment” (ASHRAE Standard 55-2010). In this approach, the focus is on how the occupant feels in a temperature-based environment. The simulation of thermal comfort represents the conservation of energy between the environment and the human body. The heat gain or loss between our body and the environment occurs through radiation, convection, conduction, respiration and evaporation as shown in the figure.
To express the energy balance equation in a simple way;
M-W=E+R+C+K+S
M; metabolic heat production, W, heat production by doing external work, E; by evaporation; radiation, C; convection, K; conductivity refers to heat transfer, while S refers to heat stored in the body.
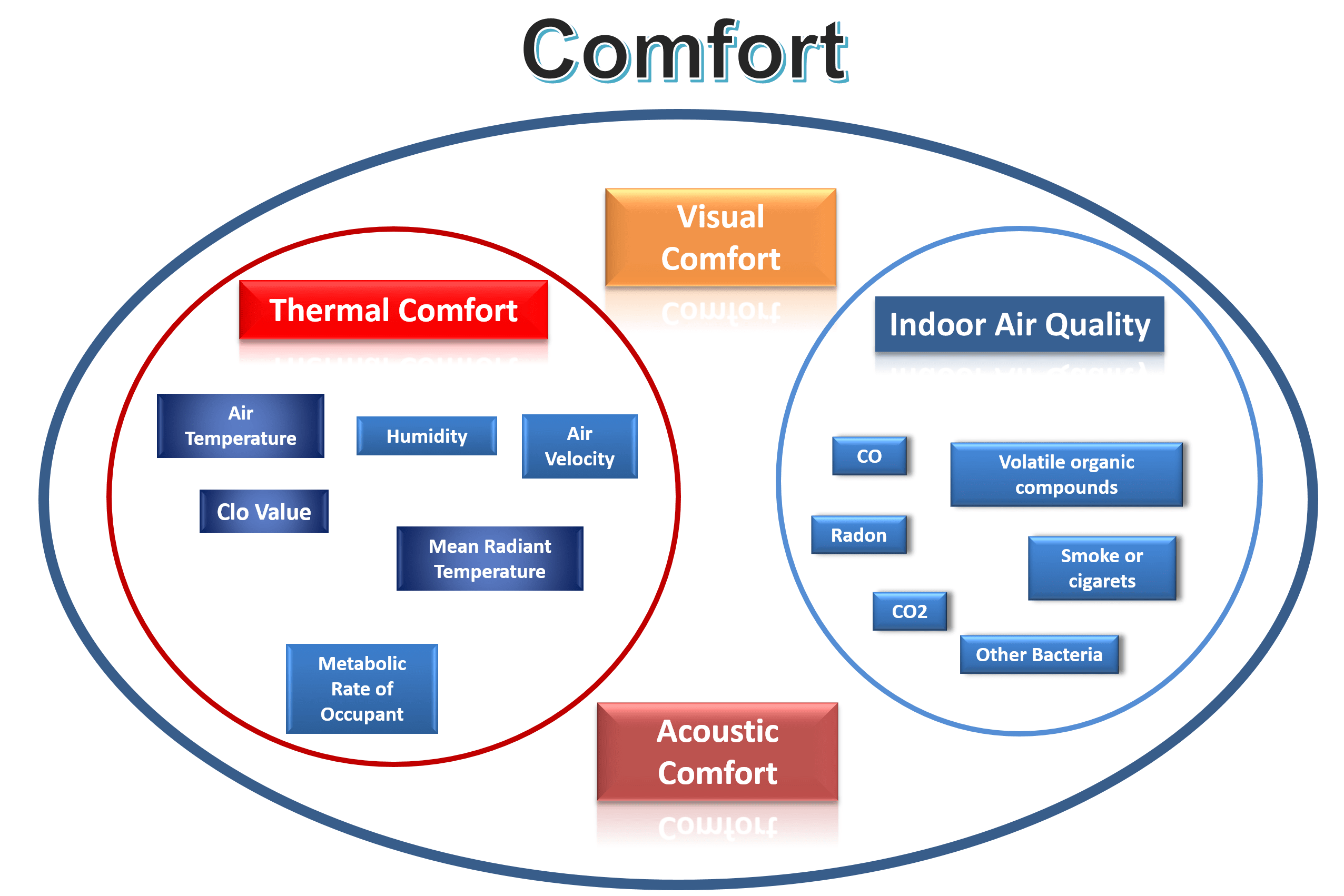
Many methods are used in the evaluation of indoor thermal comfort results. It is derived from P.O. Fanger, the most widely accepted in the literature and used by Alkazar. A total of 6 different parameters are used in this method to calculate predicted mean vote (PMV) and predicted percentage dissatisfied . Four of these belong to indoor conditions, while the remaining two parameters depend on human metabolic heat production and thermal conductivity of clothing.
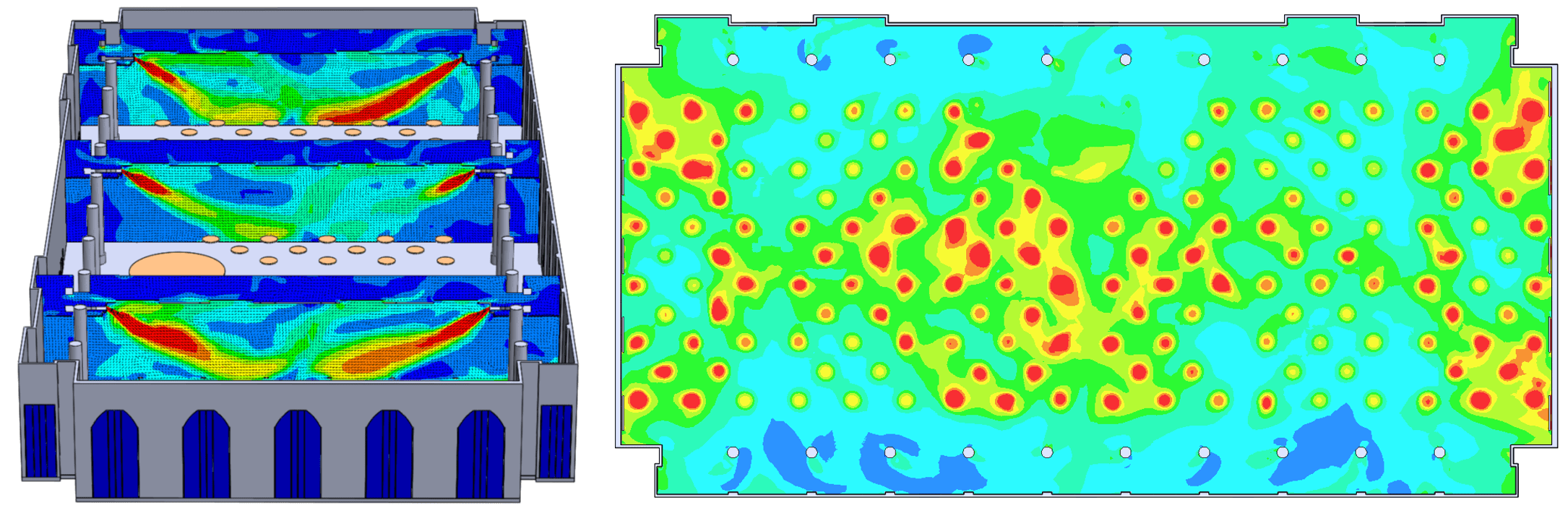
When calculating thermal comfort within the space, many different software can quickly analyze the comfort of a simple room. Calculation of air velocity, which is one of the critical parameters in these analyzes, is a difficult issue in numerical terms even in today’s computer development conditions. air velocity, air temperature, average radiation temperature and relative humidity. In terms of thermal comfort, the air conditioning speed should not exceed 0.25 m / s within the comfort zone, so that users cannot cool down in summer in an office environment. This will of course vary according to psychological, physiological and cultural habits. But a designer should create an environment that is capable of meeting change for everyone, not the ideal space design for everyone.
In the first stage, the design has advantages for passive systems with architectural groups and then for active systems with mechanical design teams. Thus, increasing the awareness of the design quality and the extent to which the needs can be met are tested numerically.
While thermal comfort is a phenomenon related to air conditioning in the space, indoor air quality is based on ventilation principles. Indoor air quality is a fact that requires the right design conditions in terms of health before it affects comfort. For example, if you experience headaches, inability to breathe, lack of concentration, drowsiness or frequent illness, you may be left in an inefficient ventilation after a certain period of time in the office where you work. Naturally and mechanically determined ventilation principles are based on the amount of clean air that must be recirculated in a per-person environment. For example, mixing air in an office environment can be replaced by fresh air (outdoor air) 2-3 times to meet the required conditions. If this cycle is not provided, especially the concentration of indoor CO2 and other pollutants (odors, particulates, etc.) in certain locations (which may also depend entirely on the interior design) may cause you to have a headache at a time when the two tables work behind you with pleasure.

Poor indoor air quality reduces the hard working productivity of businesses in the office environment. For schools, it becomes important for students to weaken perception after a certain period of time. While you are standing in a conference room, the show is very good, but the feeling of uncomfortable stuffiness prevents you from wanting to go to the same place again.
Alkazar acts simultaneously with architectural and mechanical design and sometimes with product suppliers (table, chair, cabinet etc.) visualizes the design templates in which the ideal air quality can be created within the space.